Content Scanning Configuration
The content scanning feature on CyberHound is a security service designed to enhance network protection by analyzing and filtering web traffic in real-time. Utilizing HTTPS inspection, CyberHound can intercept encrypted network traffic, decrypt it, and then scan the content against a predefined set of words, lists, phrases, and patterns. This allows the system to identify and block access to potentially harmful or inappropriate content before it reaches the user. By focusing on specific keywords and patterns, the content scanning feature ensures that organizations can enforce their policies, protect against threats, and maintain a safe and secure online environment. This capability is particularly valuable for educational institutions and enterprises, where maintaining control over accessible content is crucial for safeguarding users and ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
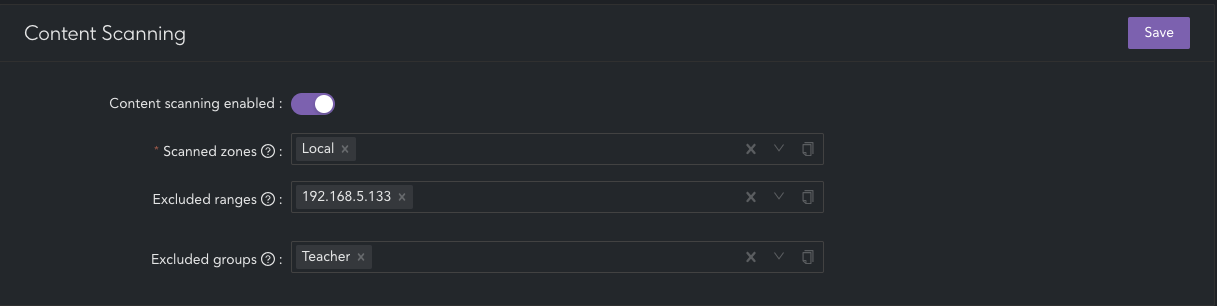
Enable Content Scanning
The CyberEdge content scanning engine is specifically designed to scan particular internet applications for matching content. To accomplish this, the relevant applications need to be subjected to HTTPS inspection. This configuration guide offers comprehensive instructions for setting up content scanning, including how to bypass HTTPS inspection and scanning for networks and users where it is not needed. Before enabling content scanning, it is essential to deploy the client certificate to support HTTPS inspection. To enable content scanning navigate to:
- Content Scanning > General
- Set the toggle to "enabled"
- Scanned Zones: Choose the source network zone for the devices to be scanned. All devices within this zone (unless specifically excluded) will have the relevant content scanning applications subjected to HTTPS inspection and analyzed by the content scanning engine. It is mandatory to specify at least one source zone but supports multiple network zones
- Exclude Ranges: Identify any networks or IP addresses within the configured scanned zones that should be excluded from HTTPS inspection and content scanning
- Exclude Ranges: In certain network topologies, excluding specific networks or IP addresses may be challenging. In such cases, opt to bypass HTTPS content scanning by selecting specific user groups
- Click "Save"
- Click "Save" and "Apply" changes
Applying changes when enabling or disabling content scanning will trigger a proxy service restart. It is recommended to schedule this change at a time that minimizes potential service disruption to the network.
Detailed information on the applications HTTPS inspected and scanned by the content scanning can be found here.
Warning
- Before enabling content scanning, it is necessary to deploy the client certificate on devices that require HTTPS inspection; otherwise, applications will experience certificate errors in the browser and prevent its use
- Applying changes when enabling or disabling content scanning will trigger a proxy service restart. It is recommended to schedule this change at a time that minimizes potential service disruption to the network
Supported Applications
Content scanning is compatible with a range of internet-based applications. Below is a list of the supported applications and browsers:
Supported Applications
- Google Search: Google search - (Supported web browsers Chrome, Safari, FireFox, Edge)
- Bing Search: Bing search - (Supported web browsers Chrome, Safari, FireFox, Edge)
- DuckDuckGo Search: DuckDuckGo search - (Supported web browsers Chrome, Safari, FireFox, Edge)
- Wikipedia Search: Wikipedia search - (Supported web browsers Chrome, Safari, FireFox, Edge)
Disable Content Scanning
To disable content scanning function completely navigate to:
- Content Scanning > General
- Set the toggle to "disabled"
- Click "Save"
- Click "Save" and "Apply" changes
Warning
- Applying changes when enabling or disabling content scanning will trigger a proxy service restart. It is recommended to schedule this change at a time that minimizes potential service disruption to the network